Author: admin
Routing Numbers and Transit Numbers
Canadian Transit Number:
Canadian Transit Number is a 9 character code used for routing of cheques (checks) and paper instruments in the banking industry. This code identifies the branch (and bank/credit union) on which the cheque is drawn. It is also known as check routing number and MICR Code.
The format of check transit number – XXXXX–YYY
The first 5 digit is called branch transit number and identifies the exact branch of the bank. YYY is the institution code which identifies the bank or credit union. There is a dash (or hyphen) separating the branch code and institution code. As a general rule, bank institution numbers start with 0, 2, 3, or 6, while Credit Union and Caisse Populaire institution numbers start with 8, and Trust Company institution numbers with 5. The big 4 banks have the following institution code –
001 – Bank of Montreal
002 – Bank of Nova Scotia
003 – Royal Bank of Canada
004 – TD Canada Trust
Canadian Routing Number:
Canadian Routing Number is a 9 digit code used for electronic fund transfers (EFT) such as direct deposits, electronic payments, etc. The Routing Number are also formed using the branch code and bank code discussed above.
Routing Number Format
Routing number (EFT Code) is a 9 digit code comprising of a leading zero (0), the institution number (YYY), then the branch number (XXXXX). For example if a cheque MICR code is XXXXX-YYY, the corresponding EFT code would be 0YYYXXXXX.
If you want to setup a direct deposit or want to make a electronic fund transfer to someone’s account, the sender’s bank will ask for following three things –
1. Recipient’s Full Name
2. Recipient’s Account Number
3. Routing Number (and possibly the bank name)
Find Routing Number: Search for the routing number using our routing number search tool below –
For International Transfers, bank will also ask for the swift code (also called BIC code) along with the above three details.
Difference between Routing Number and Transit Number:
Both routing number and transit numbers are formed using the branch code and institution code. However, there is a difference in the format as discussed above. The term routing number is used in connection with the electronic fund transfers (EFT) and thus also known as EFT Code while the transit number is used usually in connection with the paper instruments such as cheques. You can also find transit number on the cheque issued to you by your bank. The transit number is also called MICR code.
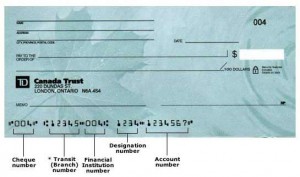
Note: If a cheque code is XXXXX-YYY, the corresponding EFT code would be 0YYYXXXXX.
If you have any questions on the electronic payment or routing number, please leave a comment below. We’d be happy to help!
Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) Routing Numbers
CIBC Routing Number
Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBC) is one of the biggest banks in Canada. You can find routing transit number for all branches of CIBC bank in Canada. Use the CIBC Routing Number Search tool or just click on the name of the city where your CIBC branch is situated. Routing Numbers are 9 digit bank identification number which are used for initiating direct debit, wire transfers, check routing and other electronic payments. You can also locate the routing number on the check book issued by your bank.
Canada’s Top Banks’ Ratings Downgraded to ‘Negative’ by S&P
Canada’s top banks got a “negative” ratings from ratings agency S&P over concerns about the federal government’s stance on possible bailouts in the future.
The decision is taken on the concern that the government might be reluctant to “bail out” top banks with tax-payers money if another financial meltdown (similar to 2008-2009) happens in the future. This virtually takes away the “too big to fail” status from the banks and make them susceptible to liquidation in another event of financial meltdown.
“The outlook revision reflects our expectation of reduced potential for extraordinary government support,” wrote credit analyst Lidia Parfeniuk in a note released Friday (8th Aug 2014).
The negative outlook covered all of the major Canadian Banks – Royal Bank of Canada (RBC), Toronto-Dominion Bank (TD Canada Trust), Bank of Nova Scotia (Scotia Bank), Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (CIBM), Bank of Montreal (BMO) and National Bank of Canada (NBC).
This is important to note that Canadian Banks are counted among the world’s most stable banks. Despite the downgrades, the TSX financial sector was ahead 0.55 per cent on Monday, with all of the major bank stocks higher.
How to Resolve a Problem with your Bank
If you have a problem or complaint at your bank or trust company, you can follow these steps to get help.
Important Note:
Every time you talk to someone, write down their name, the date you talked to them, what they told you, and if some part of the problem was fixed. Keep your papers about the problem. If someone asks you to give them the papers, give them a copy and keep the original paper.
You must do the steps in order (you can’t skip a step).
Step 1
Explain your problem to the staff at your branch. You can ask to talk to a supervisor or a manager of the bank branch.
Step 2
If the branch staff don’t fix your problem, ask them for their brochure about complaints. The brochure has telephone numbers for senior managers or customer care centres. Call the number and explain your problem. Many banks also have their own ombudsman to help customers with complaints.
Step 3
If you still have a problem, you can call an independent ombudsman who doesn’t work for the bank. If your bank account is at RBC Royal Bank, call ADR Chambers at 1-877-307-0014. For all other banks, call the Ombudsman for Banking Services and Investments at 1-888-451-4519. The ombudsman will talk to you and to the bank, and look at your papers about the problem. The ombudsman will decide what is fair and tell the bank to do it.
You can also go to court to get a problem fixed, but it is more expensive. Also, if you go to court, you can’t use the ombudsman.
If you have a problem at a credit union or caisse populaire, ask to speak to the manager. If the manager doesn’t solve your problem, ask what to do about complaints. The provinces have government offices that can help you with a problem after you try to fix it with the credit union or caisse.
Economic Action Plan 2014 to Benefit New Brunswick and Canada
Speaking to the Greater Moncton Chamber of Commerce, Finance Minister Joe Oliver today highlighted the many benefits of the Harper Government’s Economic Action Plan 2014 for New Brunswick and the rest of Canada. He also reaffirmed the Government’s top priority of creating jobs and economic growth through low taxes and enhanced trade, while remaining on track for a balanced budget in 2015.
Quick Facts about Economic Action Plan 2014
- Since the Government introduced the Economic Action Plan to respond to the global recession, Canada has performed better than most developed countries.
- Both the International Monetary Fund and the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development expect Canada to be among the strongest growing economies in the Group of Seven (G-7) over this year and next.
- New Brunswick will receive $860 million over 10 years in dedicated federal funding, including $390 million under the New Building Canada Fund and $470 million under the federal Gas Tax Fund.
- On June 20th, the Prime Minister announced that New Brunswick’s Propel ICT has been chosen to advance in the selection process under the Canada Accelerator and Incubator Program.
- Under the Canada Research Chairs program, the Government provides annual support totaling $1.3 million for 10 leading researchers based in Moncton post-secondary institutions.
“To keep New Brunswick and Canada strong, we must build on our firm economic and fiscal fundamentals, and a track record that is the envy of many other countries. Honouring this commitment, including a return to budgetary balance in 2015, will help foster a growing, healthy economy that creates stable, well-paying jobs, right across this country.”
Download full economic budget plan 2014.
CDIC Insurance for Joint Deposits – How it is Calculated?
CDIC (Canadian Deposit Insurance Corporation) insures eligible deposits at each CDIC member institution up to a maximum of $100,000 (principal and interest combined) per depositor (or, in the case of joint deposits, per set of joint owners), in each of the following:
- Savings held in one name
- Joint deposits (savings held in more than one name)
- Savings held in trust for another person
- Savings held in Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSPs)
- Savings held in Registered Retirement Income Funds (RRIFs)
- Savings held in Tax-Free Savings Accounts (TFSAs)
- Money held for paying realty taxes on mortgaged property
To be eligible for deposit insurance, deposits must be payable in Canada and in Canadian currency. As a general rule, a deposit is considered to be payable in Canada if it is held at a branch or office of a CDIC member institution in Canada.
Eligible deposits include savings accounts, chequing accounts, GICs or other term deposits with an original term to maturity of 5 years or less, money orders, certified cheques, and bank drafts issued by CDIC members.
As stated above, eligible joint deposits are insured separately from deposits in each person’s own name alone at the same member institution, up to a maximum of $100,000 (principal and interest combined). However, this deposit insurance is payable per set of joint depositors; that is, the joint owners together receive a single deposit insurance payment of up to $100,000.
To be eligible for separate CDIC insurance coverage, the following information about a joint deposit has to appear on the records of the member institution:
- a statement that the deposits are owned jointly; and
- the name and address of each of the joint owners.
It is important to note that each person identified as a joint owner must have a genuine ownership interest in the deposit for separate deposit insurance protection to apply. The creation of artificial joint deposits for the sole purpose of obtaining additional deposit insurance protection is contrary to the intent of the CDIC Act.
Source: CDIC Website
TD Canada Trust Routing Numbers
TD Canada Trust is the personal, small business and commercial banking operation of the Toronto-Dominion Bank (TD) in Canada. TD Canada Trust offers a range of financial services and products to more than 10 million Canadian customers through more than 1,100 branches and 2,600 “Green Machine” ABMs. (Automated Banking Machines)
The current TD Canada Trust division was formed after TD’s acquisition of Canada Trust in 2000. All new and most existing accounts are officially issued by TD Bank (Institution Number: 004), although Canada Trust (Institution Number: 509) remains a separate subsidiary entity, and remains the issuer of accounts opened at that institution prior to the merger.
You can find routing number for all branches of TD Canada Trust using the below table –
Montreal Trust Company Routing Transit Numbers
Montreal Trust Company of Canada was originally established in 1889 as the Montreal Safe Company and became a trust company only a few years later. In 1994, the Montreal Trust Company became a member of the Scotia Group of Companies when Scotiabank completed its acquisition.
Mailing address for Montreal Trust Company
Executive Offices, Scotia Plaza, 9th Floor
44 King Street W
Toronto, Ontario
Canada M5H 1H1